Almost all data sources require user authentication to access data. The most prevalent methods include OAuth2 and API key authentication.
The Authentication component enables you to configure how the access token is acquired from the connector user. In other words, it defines how the authentication flow to the connector works.
To ensure secure storage of access tokens, it’s advised to configure the authentication component instead of using access tokens directly in the configuration.
Note
If the data source does not require authentication, you don’t need to include an authentication component in your configuration.
Supported authentication methods
Our connectors support all the most common authentication methods:
Authetication type | Type defined in the configuration |
|---|---|
API key (header or query param) |
|
OAuth2 |
|
OAuth1 |
|
Basic authentication (username and password) |
|
Session-based authentication (cookies) |
|
JSON Web Token |
|
Amazon S3 |
|
Microsoft Exchange |
|
Below you can find documentation for the most common authentication methods and authentication configurations.
API key authentication
API key authentication flow is the method used to authenticate to APIs that provide an API key or an access token, which must be included in each request.
The API key authentication type is configured with type: "user_input" in the JSON configuration.
In this authentication type, you must define one or multiple input fields to be shown when connecting to the data source.
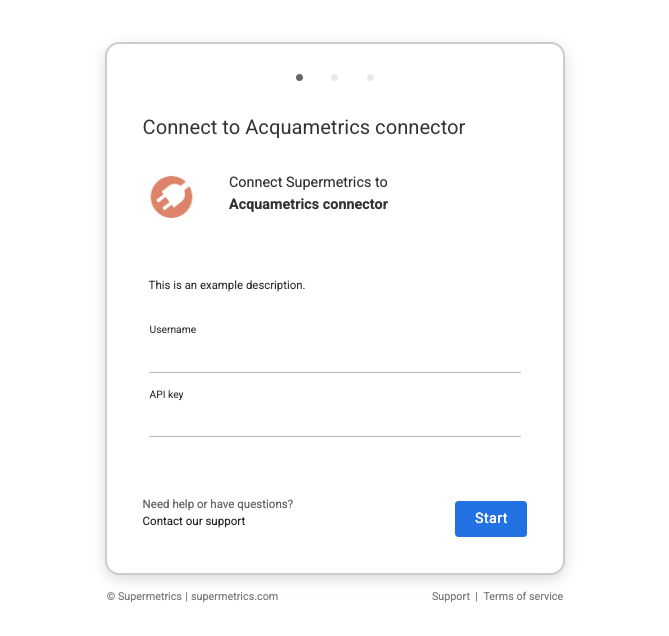
Configuring API key authentication
API key authentication is configured with type user_input in the connector configuration. User input authentication allows you to request the user to input necessary credentials during the authentication flow, which you can later use in API requests through placeholders.
Below, you can find an example where we are defining three input fields for the authentication flow:
Account name (Id:
account_name)API key (Id:
api_key)Company name (Id:
company_input)
Account name and Company name are defined as text fields, and the API key is defined as a password. As the API key is a password, the typed value is hidden. The configuration for the authentication would look like this:
{
...
"authentication": {
"type": "user_input",
"description": "This is a description for API key authentication"
"userInputs": [
{
"id": "account_name",
"label": "Account name",
"type": "text"
},
{
"id": "api_key",
"label": "API key",
"type": "password"
},
{
"id": "company_input",
"label": "Company name",
"type": "text"
}
]
}
...
} In this case, the Supermetrics data source connection flow would look like this:
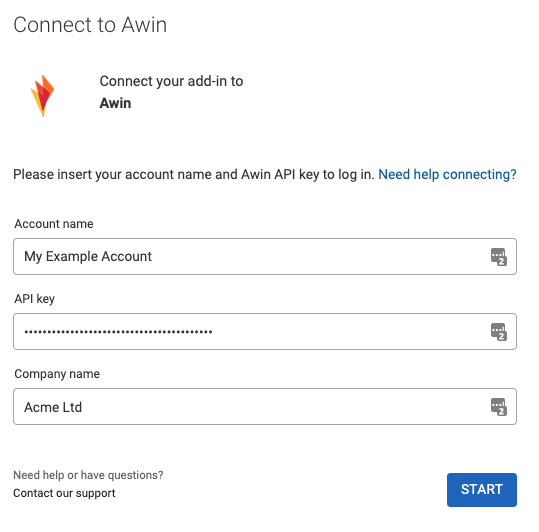
Storing inputted values in Data source user
To have values inputted by the user stored securely, and to use these values later in the configuration, we need to define these values to be stored using the Data source user component.
Below you can find an example Data source user configuration for the above authentication. In this example configuration:
The API key inputted by the user is stored as
accessTokenand it’s used to identify users when making requests to APIs, and it’s not publicly exposed.The Account name inputted by the user is stored as
labelso users can identify different authentications from each other.A Data Source User ID is generated using the
{{identity()}}placeholder to generate a unique ID for each authentication.The company name is stored under additional properties with the ID
company
An example of full authentication and data source user configuration for the above would look like this:
"authentication": {
"type": "user_input",
"description": "This is a configured login description",
"userInputs": [
{
"id": "account_name",
"label": "Account name",
"type": "text"
},
{
"id": "api_key",
"label": "API key",
"type": "password"
},
{
"id": "company_input",
"label": "Company name",
"type": "text"
}
]
},
"dataSourceUser": {
"userInfo": {
"id": {
"source": "static",
"value": "{{ identity() }}"
},
"label": {
"source": "userInput",
"value": "account_name"
},
"accessToken": {
"source": "userInput",
"value": "api_key"
},
"properties": [
{
"id": "company",
"source": "userInput",
"value": "company_input"
}
]
}
}Using user-inputted values in requests
To use the values the user has inputted during the authentication, and which we stored under data source user, we should use placeholders. These placeholders can be used under request object in any part of the configuration. Within request object, you can define the placeholder to be used in:
Request URLs
Request headers or parameters
With the above configuration, you would have the following placeholders available to use:
{{user.access_token}}to use the API key inputted by the user{{user.id}}to use the generated unique ID value{{user.label}}to use the Account name inputted by the user{{user.properties.company}}to use the Company name inputted by the user
An example usage of company name in the request URL under and API key in the request headers could look like this:
"request": {
"method": "GET",
"url": "https://{{user.properties.company}}.exampleAPI.com/products",
"headers": [
{
"name": "api_key",
"value": "{{user.access_token}}"
}
],
"response": {
"type": "JSON",
"dataRows": {
"source": "jsonPath",
"value": "$.products.*"
}
}
}OAuth2 authentication
OAuth2 is the industry-standard protocol for authorization. It allows different applications to interact with each other on behalf of the user without the user giving out their credentials.
Prerequisites for configuring OAuth2 authentication
The OAuth2 authentication requires you to create a developer application on the data source platform, and you can then use the Client ID and Client Secret provided by the platform in your configuration.
When creating the application, it usually requires you to configure a callback URL, so the data source platform knows where to send the user after successful authentication.
The callback URL used by Supermetrics is always https://supermetrics.com/login-complete .
OAuth2 authentication flow
OAuth2 authentication flow consists of a few distinct steps that we will need to configure:
authorization: The initial request to send an authorization request to the data source APItokenExchange: Request to exchange authorization code for an actual access token, as well as to receive a refresh token.Access tokens usually have a relatively short lifetime, but they can be programmatically refreshed using a refresh token.
refresh: Request to fetch a new token before the old one expires.
Template OAuth2 configuration
Below you can find a template configuration that you can fill in with your own information for an easier start:
{
"authentication": {
"type": "oauth2",
"description": "Example description shown to users in the authentication screen.",
"oauth2": {
"clientId": "[client ID]",
"clientSecret": "[client Secret]",
"tokenLifetime": 3600,
"tokenJsonPath": "$[path to access token in JSON response]",
"authorization": {
"request": {
"url": "[url to authorization endpoint]",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "[parameter name]",
"value": "[parameter value]"
}
]
}
},
"tokenExchange": {
"request": {
"method": "POST",
"url": "[url to token exchange endpoint]",
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "authorization_code"
},
{
"name": "code",
"value": "{{oauth2.code}}"
},
{
"name": "client_id",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_id}}"
},
{
"name": "client_secret",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_secret}}"
},
{
"name": "redirect_uri",
"value": "{{oauth2.callback_url}}/"
}
]
}
}
},
"refresh": {
"request": {
"method": "POST",
"url": "[url to token refresh endpoint]",
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "refresh_token"
},
{
"name": "refresh_token",
"value": "{{oauth2.refresh_token}}"
},
{
"name": "client_id",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_id}}"
},
{
"name": "client_secret",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_secret}}"
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
}Configuring OAuth2 authentication
We’ll instruct you to configure OAuth2 authentication flow using Spotify Ads API as an example. The authentication details for the Spotify Ads API can be found here:
To configure OAuth2 authentication to Spotify Ads, we need to:
Add
authenticationcomponent with typeoauth2.Add Client ID and Client Secret as encrypted values.
Configure the Authentication endpoint and request under the
authorizationobject.Define the JSON path to get the token in the response and define the lifetime for the token.
Token exchange under
tokenExchangeobject.Token refresh under
tokenRefreshobject.
Base configuration for OAuth2 authentication
Let’s start by defining the base configuration for OAuth2 authentication type:
"authentication": {
"type": "oauth2",
"description": "Description shown to users during the authentication flow",
"oauth2": {
...
}
}Client ID and Client Secret
First, we need to input Client ID and Client Secret for the app that we’ve registered to the data source platform.
Values for Client ID and Secret need to be encrypted before they are inputted to the configuration, as we don’t want to store any sensitive information directly in the configuration. Encryption can be done in “Secret encryption” section within the Connector builder user interface.
Once we have encrypted the credentials and inputted them into the configuration, the config should look like this:
"authentication": {
"type": "oauth2",
"description": "Description shown to users during the authentication flow",
"oauth2": {
"clientID": "[encrypted client ID]",
"clientSecret": "[encrypted client secret]",
...
}
}Authorization
Next, we’ll configure the authorization object under the oauth2 object to define how the first authentication request is done. You can see the documentation on how Spotify Ads API requires the authentication request to be made in Spotify’s documentation: Authenticate your Ads Manager account
The authentication request is done by adding the request object with the required url and parameters. You’ll need to match the URL and parameters to the API you’re working with, which in this case are the following:
client_id
response_type
redirect_uri
state (This is a parameter required by Supermetrics and provides protection against attacks such as cross-site request forgery (see RFC-6749))
The request url is configured as a string, and the parameters as an array, like in the example below. For most of the values, we want to use ready placeholders to ensure the values will always be correct. The configuration would look like this:
"authorization": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/authorize/",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "client_id",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_id}}"
},
{
"name": "response_type",
"value": "code"
},
{
"name": "redirect_uri",
"value": "{{oauth2.callback_url}}"
},
{
"name": "state",
"value": "{{oauth2.state}}"
}
]
}
}Token exchange
Next, we need to configure how the authorization code received after user authorization is exchanged to the access token. This can be done in the Spotify Ads API by making a POST request to the endpoint https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token with the following details:
Base64 encoded client ID and client secret as
Authorizationheader.Request body with following parameters:
grant_typewith string valueauthorization_codecodewith the code received from the previous requestredirect_uriwith the callback URL of Supermetrics
This is configured as request object under tokenExchange object, and we will use placeholders for most of the values, and placeholder operations to have client ID and secret encoded with Base64 encoding.
The configuration will look like this:
"tokenExchange": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token",
"method": "POST",
"headers": [
{
"name": "Authorization",
"value": "{{base64(oauth2.client_id, ':', oauth2.client_secret)}}"
}
],
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "authorization_code"
},
{
"name": "code",
"value": "{{oauth2.code}}"
},
{
"name": "redirect_uri",
"value": "{{oauth2.callback_url"
}
]
}
}Token JSONpath and Token lifetime
Next, we will configure JSONpath to find the token from the response and the lifetime for the token. After calling the Spotify Ads API to authenticate, the response will look like this:
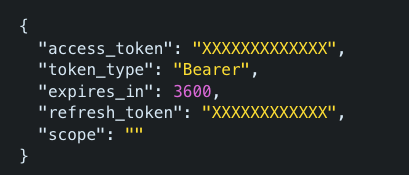
We can see that the access token is provided in the parameter access_token, refresh token in refresh_token, and the lifetime of the token is 3600 seconds.
To find the access token, to know when to refresh it, and what refresh token to use, we need to configure the tokenJsonPath and tokenLifeTime properties under the oauth2 object and the refreshTokenJsonPath property under the tokenExchange object in the connector configuration.
tokenJsonPathis configured as a string with JSONpath to the fieldaccess_tokenin the response.tokenLifeTimeis configured as an integer with the number of seconds how long the token is valid.Note: Token lifetime can also be defined to be read dynamically from the response using
expiresInJsonPathproperty
refreshTokenJsonPathis configured as a string with JSONpath to the fieldrefresh_tokenin the response.Note: While the other configuration comes directly under
oauth2object, the refresh token configuration should be done undertokenExchange.
The configuration will look like this:
{
"authentication": {
"type": "oauth2",
"description": "Description shown to users during the authentication flow",
"oauth2": {
"clientId": "[encrypted client ID]",
"clientSecret": "[encrypted client secret]",
"authorization": {
"request": {
...
}
},
"tokenExchange": {
"request": {
...
},
"refreshTokenJsonPath": "$.refresh_token"
},
"tokenJsonPath": "$.access_token",
"tokenLifetime": 3600
}
}
}Now you should already have a finalized authentication where you have received the actual access token from the API, which you can already start using in reporting requests!
However, this access token is set to expire after a short time by the API, so we want to next configure the token refresh flow to ensure the token is automatically refreshed by our system.
Token refresh
Access tokens granted by OAuth2 flow are commonly set to expire after short time. In Shopify Ads API, the lifetime of the token is 3600 seconds which is 60 minutes. In order to ensure you don’t need to authenticate again after every 60 minutes, we want to configure an automatic token refresh flow.
This is done by configuring the tokenRefresh object under the oauth2 configuration. Under tokenRefresh, we can define a request to be made to refresh the token.
The Spotify Ads API requires a POST request to the endpoint https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token with the following details:
Base64 encoded client ID and client secret as
Authorizationheader.Request body with following parameters:
grant_typewith string valuerefresh_tokenrefresh_tokenwith the refresh token received from the authentication step
The configuration for refresh token will look like this:
"refresh": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token",
"method": "POST",
"headers": [
{
"name": "Authorization",
"value": "{{base64(oauth2.client_id, ':', oauth2.client_secret)}}"
}
],
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "refresh_token"
},
{
"name": "refresh_token",
"value": "{{oauth2.refresh_token}}"
}
]
}
}
}Now you should have all the necessary configurations for a successful OAuth2 authentication!
Here you can see the full configuration for all the steps defined above:
{
"authentication": {
"type": "oauth2",
"description": "Description shown to users during the authentication flow",
"oauth2": {
"clientId": "[encrypted client ID]",
"clientSecret": "[encrypted client secret]",
"authorization": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/authorize/",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "client_id",
"value": "{{oauth2.client_id}}"
},
{
"name": "response_type",
"value": "code"
},
{
"name": "redirect_uri",
"value": "{{oauth2.callback_url}}"
},
{
"name": "state",
"value": "{{oauth2.state}}"
}
]
}
},
"tokenExchange": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token",
"method": "POST",
"headers": [
{
"name": "Authorization",
"value": "{{base64(oauth2.client_id, ':', oauth2.client_secret)}}"
}
],
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "authorization_code"
},
{
"name": "code",
"value": "{{oauth2.code}}"
},
{
"name": "redirect_uri",
"value": "{{oauth2.callback_url"
}
]
}
},
"refreshTokenJsonPath": "$.refresh_token"
},
"tokenJsonPath": "$.access_token",
"tokenLifetime": 3600,
"refresh": {
"request": {
"url": "https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token",
"method": "POST",
"headers": [
{
"name": "Authorization",
"value": "{{base64(oauth2.client_id, ':', oauth2.client_secret)}}"
}
],
"body": {
"type": "urlencoded_form",
"formData": [
{
"name": "grant_type",
"value": "refresh_token"
},
{
"name": "refresh_token",
"value": "{{oauth2.refresh_token}}"
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
}Using OAuth2 token in requests
Now that you have configured a successful OAuth2 flow, you can start using the OAuth2 access token in other requests. For this, we’ll be using placeholders, so we ensure all the requests will always use the latest refreshed token.
The token can be used in the request object using a placeholder {{user.access_token}} in anywhere in the configuration: in account fetching, reporting, and so on.
The configuration for it will usually look like this:
...
"request": {
"url": "http://...",
"headers": [
{
"name": "Authorization",
"value": "Bearer {{user.access_token}}"
}
],
...
}